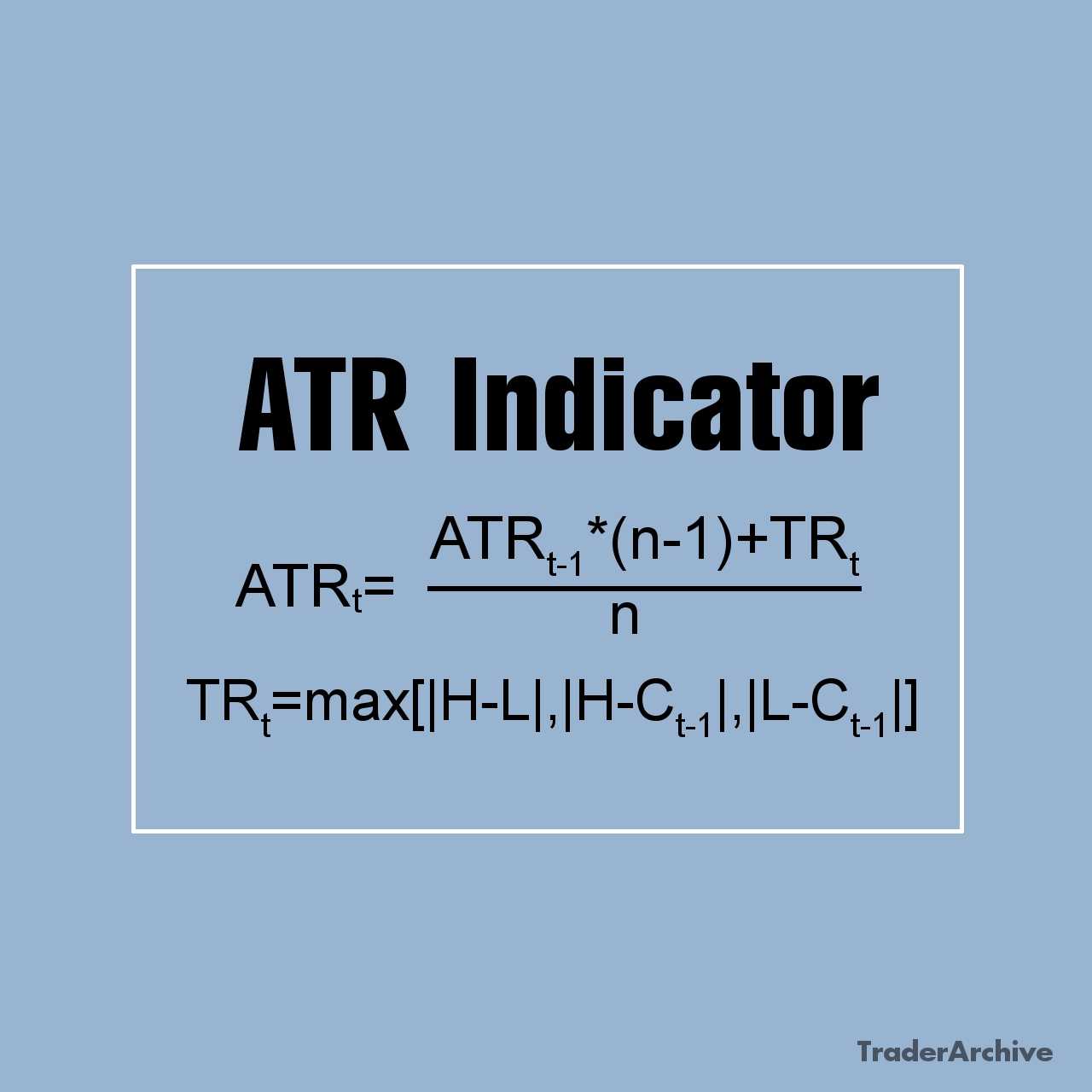
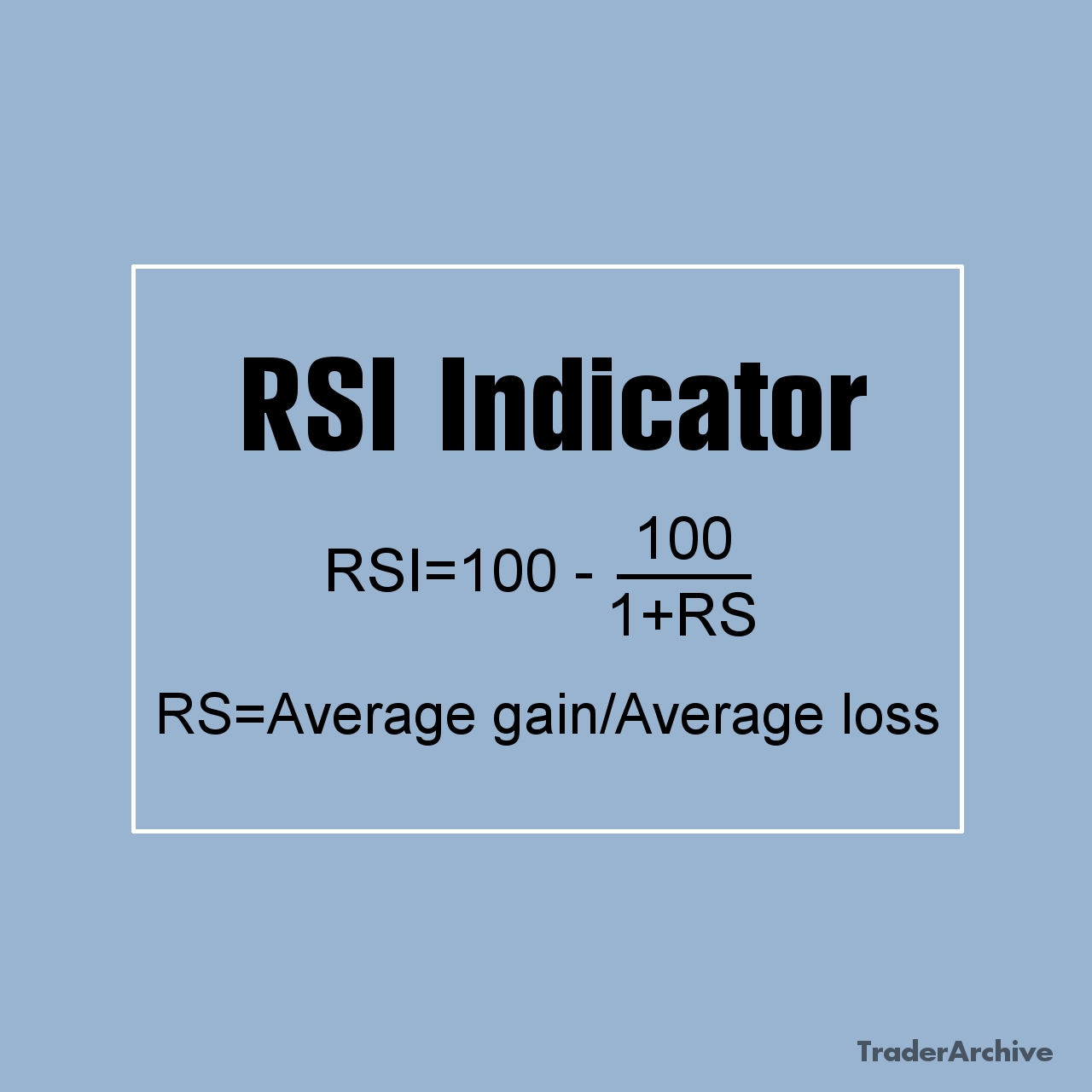
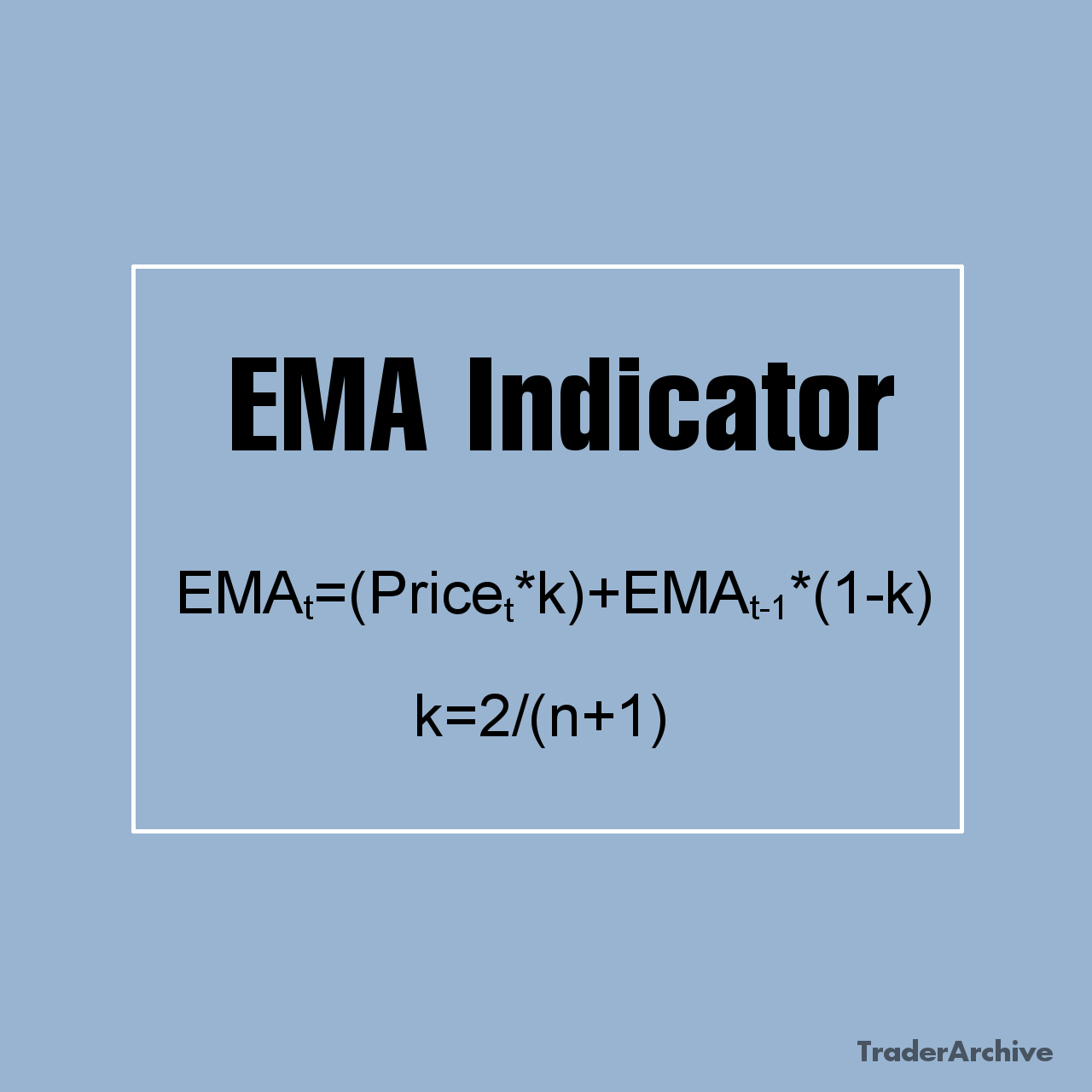
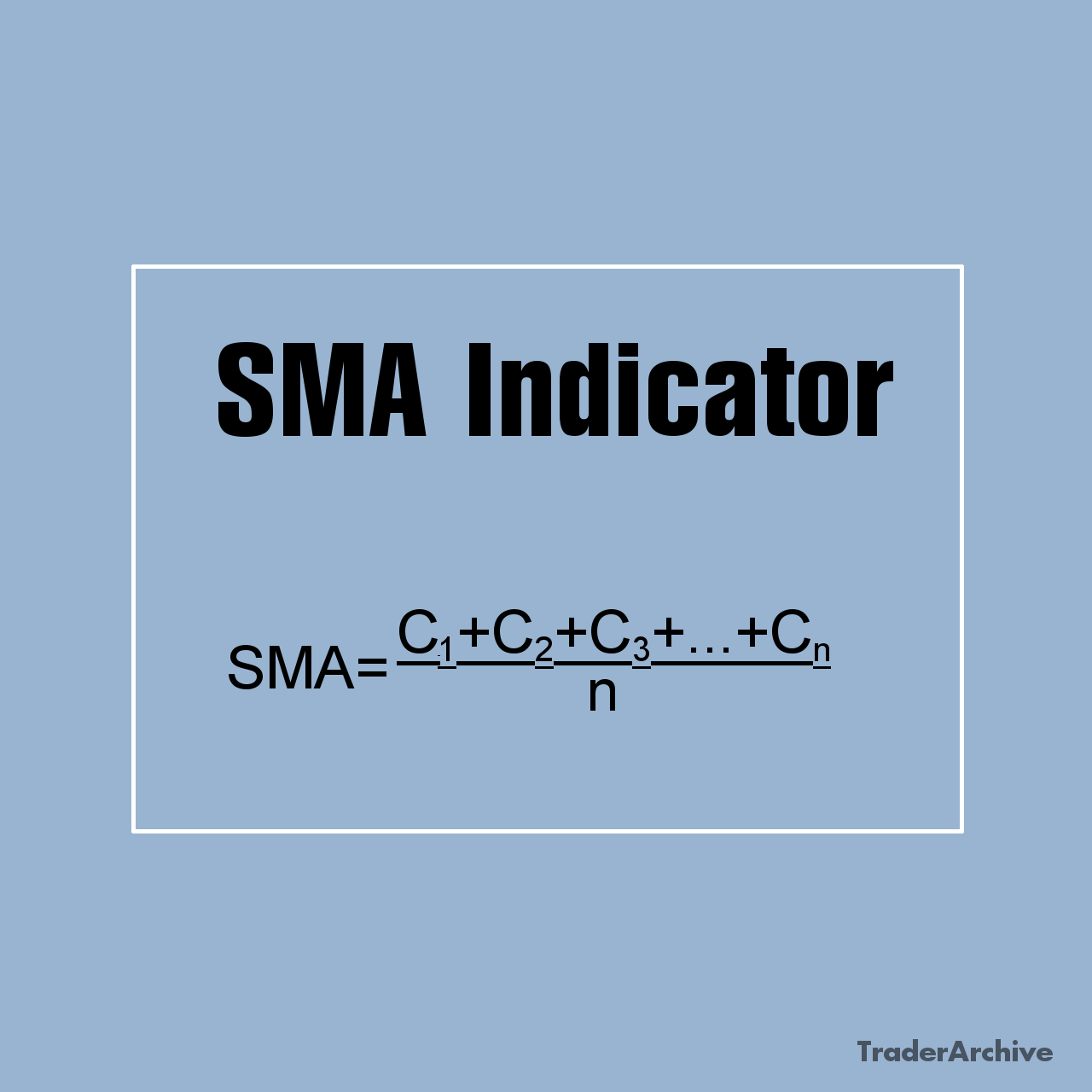
Amidst the dynamic realm of finance and investment, indices serve as vital instruments for monitoring market performance. Among these, the Hang Seng Index (HSI) stands out as a prominent fixture in the global financial panorama. Originating in 1969, the HSI has grown to symbolize the pulse of the Hong Kong stock market, commanding attention from investors worldwide. In this extensive exploration, we unravel the intricacies of the Hang Seng Index, unraveling its historical roots, constituent makeup, calculation methodology, significance, and profound influence on the global financial landscape.
History of the Hang Seng Index
The Hang Seng Index traces its origins back to November 24, 1969, when it was first introduced by the Hang Seng Bank. At its inception, the index comprised only 33 constituent stocks. Over the years, it has evolved significantly, both in terms of composition and methodology, to accurately reflect the performance of the Hong Kong stock market.
Initially, the Hang Seng Index served as a tool to measure the stock price movements of the largest and most liquid companies listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. As Hong Kong emerged as a major financial hub in Asia, the index gained prominence and became a key benchmark for investors and fund managers seeking exposure to the region.
Composition of the Hang Seng Index
The Hang Seng Index is composed of a diverse range of companies representing various sectors of the Hong Kong economy. As of 2.26.2024, the index consists of 82 constituent stocks, which are among the largest and most actively traded companies listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. Top 50 of the index:
- HSBC Holdings (0005)
- Alibaba Group Holding Limited (9988)
- Tencent Holdings Limited (0700)
- AIA Group Limited (1299)
- China Construction Bank Corporation (0939)
- China Mobile Limited (0941)
- Meituan (3690)
- Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Limited (0388)
- Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (1398)
- Bank of China Limited (3988)
- JD.com, Inc. (JD)
- Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation (SMI)
- Chow Tai Fook Jewellery Group Limited (1989)
- PetroChina Company Limited (857)
- Ping An Insurance (Group) Company of China, Ltd. (2318)
- WH Group Limited (2882)
- CNOOC Limited (883)
- China Life Insurance Company Limited (2628)
- The Bank of Communications Company Limited (3328)
- CSPC Pharmaceutical Group Limited (1099)
- Wuxi Biologics (2269)
- Sunny Optical Technology Group Co., Ltd (2382)
- AAC Technologies Holdings Limited (2018)
- Li Auto Inc. (2015)
- Xiaomi Corporation (1810)
- NetEase, Inc. (9999)
- Country Garden Holdings Company Limited (2007)
- Longfor Group Holdings Limited (168)
- Lenovo Group Limited (992)
- BYD Company Limited (1211)
- Geely Automobile Holdings Limited (175)
- Trip.com Group Limited (TCOM)
- Haidilao International Holding Ltd. (6862)
- Chow Tai Fook Jewellery Group Limited (1989)
- Li Ning Company Limited (2331)
- Anta Sports Products Limited (2020)
- Shenwan Hongyuan Securities Company Limited (2598)
- Gree Electric Appliances Inc. of Zhuhai (0661)
- Midea Group Co., Ltd. (0003)
- Zijin Mining Industry Co., Ltd. (2899)
- Sands China Ltd. (1928)
- Galaxy Entertainment Group Limited (0027)
- HK Electric Investments Limited (0006)
- Link Real Estate Investment Trust (823)
- The Hongkong and Shanghai Hotels, Limited (0004)
- Henderson Land Development Company Limited (0012)
- CK Hutchison Holdings Limited (0001)
- CK Asset Holdings Limited (1113)
- New World Development Company Limited (0017)
- Sun Hung Kai Properties Limited (0016)
The numbers in brackets next to each stock in the list represent the stock code. This code uniquely identifies each stock on the Stock Exchange of Hong Kong (SEHK). It is essential for placing orders, tracking individual stock performance, and accessing detailed information about the company. For example, “HSBC Holdings (0005)” indicates that HSBC Holdings can be identified and traded using the stock code “0005” on the SEHK.
The composition of the index is periodically reviewed to ensure that it remains representative of the Hong Kong stock market. Constituent stocks are selected based on a combination of factors, including market capitalization, trading volume, and sector representation. Companies must meet specific eligibility criteria to be considered for inclusion in the index.
The constituents of the Hang Seng Index encompass a wide spectrum of industries, including financial services, real estate, technology, consumer goods, and more. Some of the prominent companies included in the index are HSBC Holdings, Tencent Holdings, Alibaba Group, AIA Group, and CK Hutchison Holdings.
The weights of the top 10 companies in the Hang Seng Index are as follows:
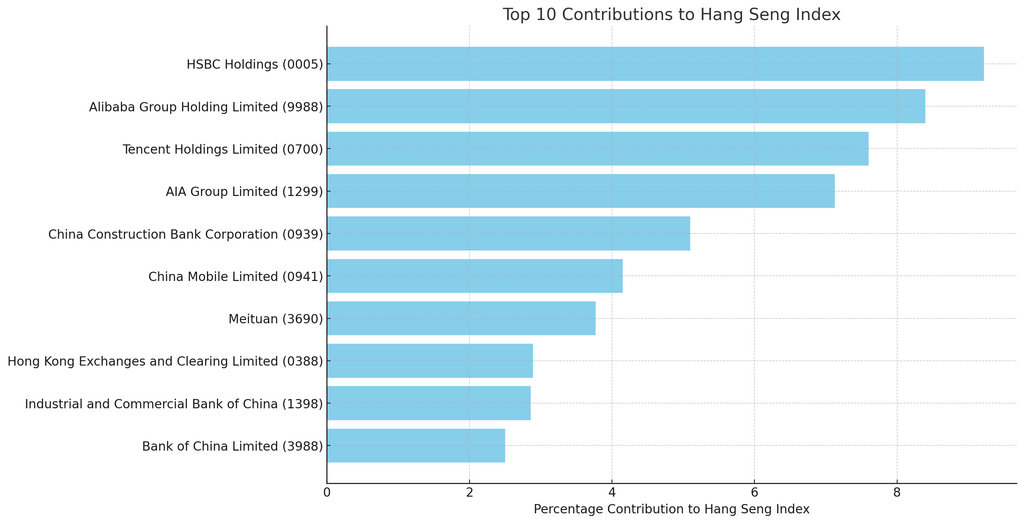
Methodology of Calculation
The calculation methodology of the Hang Seng Index is based on the market capitalization-weighted system. This means that the weight of each constituent stock in the index is determined by its market capitalization, which is calculated by multiplying the stock’s price by the number of shares outstanding.
The formula for calculating the index is as follows:
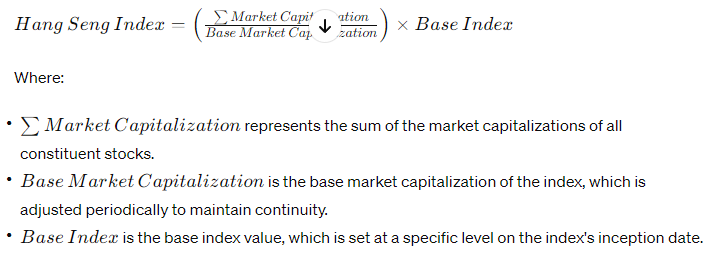
The index is calculated and disseminated in real-time throughout the trading day, providing investors with up-to-date information on the performance of the Hong Kong stock market.
Free Backtesting Spreadsheet
Significance of the Hang Seng Index
The Hang Seng Index holds significant importance for investors, traders, and financial institutions for several reasons:
- Benchmark for Performance: The index serves as a benchmark for evaluating the performance of investment portfolios, mutual funds, and other financial instruments with exposure to the Hong Kong stock market. Investors use the index as a reference point to assess the relative performance of their investments.
- Indicator of Market Sentiment: Changes in the Hang Seng Index reflect shifts in investor sentiment and market dynamics. Bullish trends indicate optimism and confidence in the market, while bearish trends signify pessimism and caution among investors.
- Global Visibility: The Hang Seng Index has gained global recognition and is closely monitored by international investors seeking exposure to Asian markets. Its performance often influences investment decisions and asset allocations by fund managers and institutional investors worldwide.
- Liquidity and Accessibility: Constituent stocks of the Hang Seng Index are among the most liquid and actively traded securities on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, making them attractive to investors seeking liquidity and accessibility to the market.
- Impact on Investment Strategies: The composition and performance of the Hang Seng Index influence various investment strategies, including index tracking, sector rotation, and quantitative trading. Investors often adjust their portfolios based on changes in the index’s constituents and weighting.
Impact of the Hang Seng Index on Global Markets
Given Hong Kong’s status as a major financial center and its interconnectedness with global markets, the Hang Seng Index has a significant impact on the broader financial landscape:
- Spillover Effects: Movements in the Hang Seng Index can have spillover effects on other regional and global markets, particularly in Asia. Changes in investor sentiment or economic fundamentals in Hong Kong may influence trading activity in neighboring markets.
- Risk Appetite and Sentiment: The performance of the Hang Seng Index often serves as a barometer of investor risk appetite and market sentiment in Asia. Positive developments or adverse events in Hong Kong can reverberate across global financial markets, affecting asset prices and volatility levels.
- Capital Flows: The Hang Seng Index attracts capital inflows from international investors seeking exposure to Asian equities. Fluctuations in the index may impact capital flows into or out of the region, affecting exchange rates, interest rates, and asset valuations.
- Intermarket Correlations: The Hang Seng Index is correlated with other major indices such as the S&P 500, Nikkei 225, and Shanghai Composite Index. Cross-market correlations influence portfolio diversification strategies and risk management practices for global investors.
Challenges and Risks
While the Hang Seng Index offers valuable insights and investment opportunities, it is not without challenges and risks:
- Market Volatility: The Hong Kong stock market, like any other financial market, is susceptible to volatility and uncertainty. Fluctuations in the Hang Seng Index can be driven by various factors, including geopolitical events, economic indicators, and regulatory changes.
- Sector Concentration: Certain sectors, such as financial services and real estate, may dominate the Hang Seng Index, leading to concentration risk. Changes in the performance of these sectors can have a disproportionate impact on the overall index.
- Market Manipulation: Despite regulatory safeguards, market manipulation and insider trading remain potential risks in the Hong Kong stock market. Instances of fraudulent activities or corporate scandals can undermine investor confidence and affect the integrity of the index.
- Currency Risk: International investors face currency risk when investing in the Hang Seng Index, as fluctuations in the Hong Kong dollar exchange rate can impact returns. Hedging strategies may be employed to mitigate currency exposure.
Final Thoughts
The Hang Seng Index occupies a central position in the global financial landscape, serving as a key barometer of the Hong Kong stock market’s performance. With its diverse composition, transparent methodology, and global significance, the index provides investors with valuable insights and investment opportunities in one of Asia’s leading financial hubs.
While the Hang Seng Index offers numerous benefits, investors should remain mindful of the inherent risks and challenges associated with investing in equities. By staying informed, diversifying their portfolios, and adhering to sound investment principles, investors can navigate the dynamic landscape of the Hong Kong stock market with confidence and prudence.
Share on Social Media: