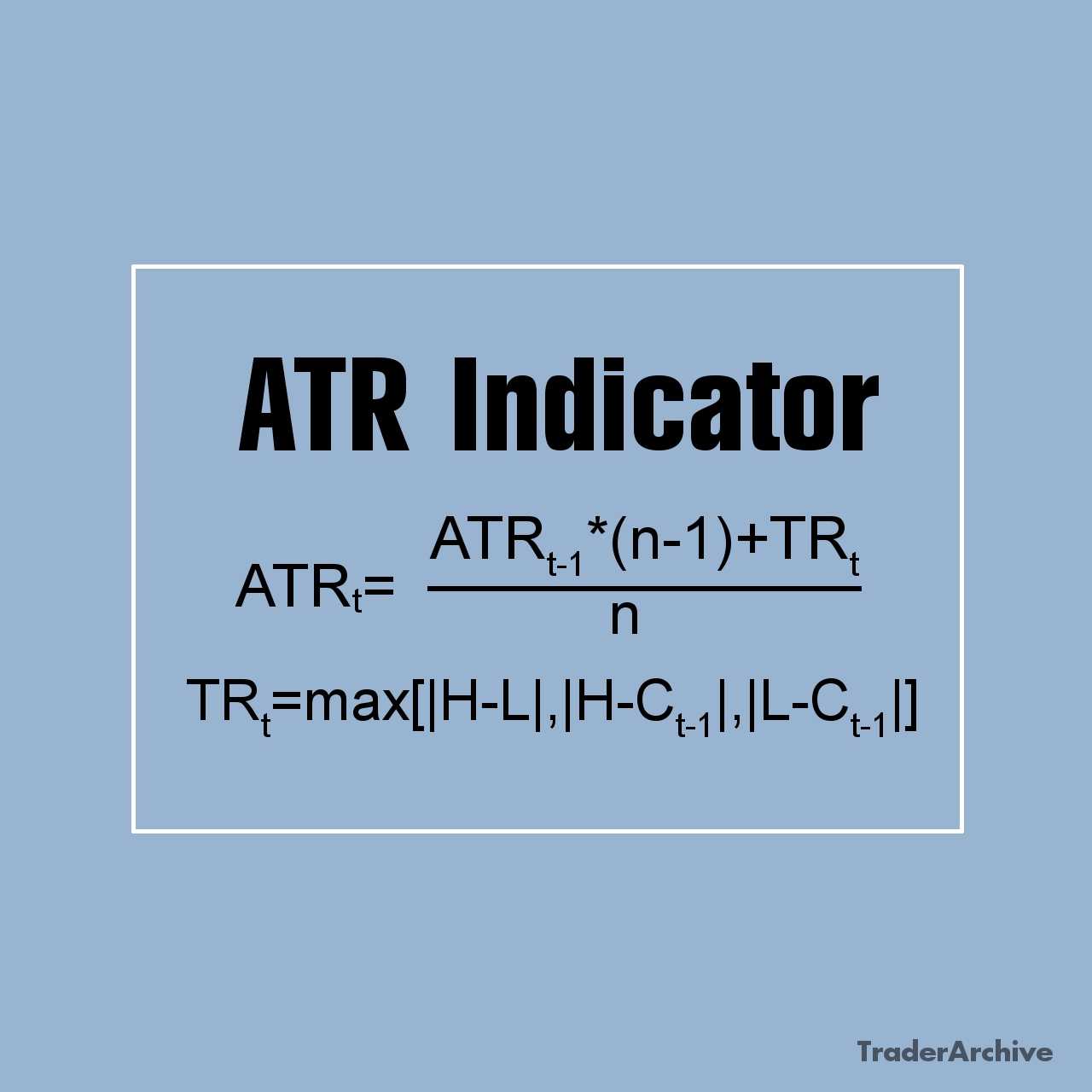
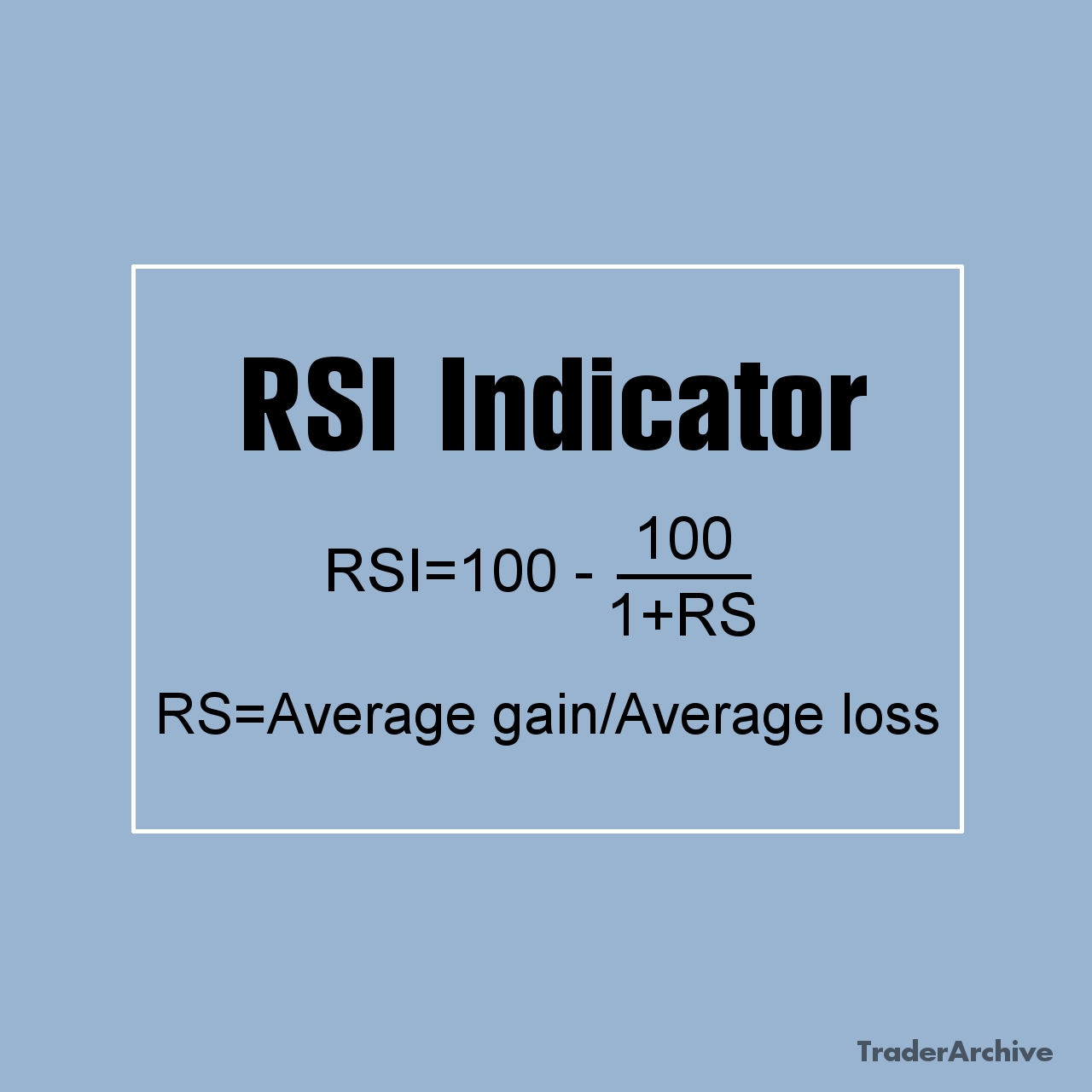
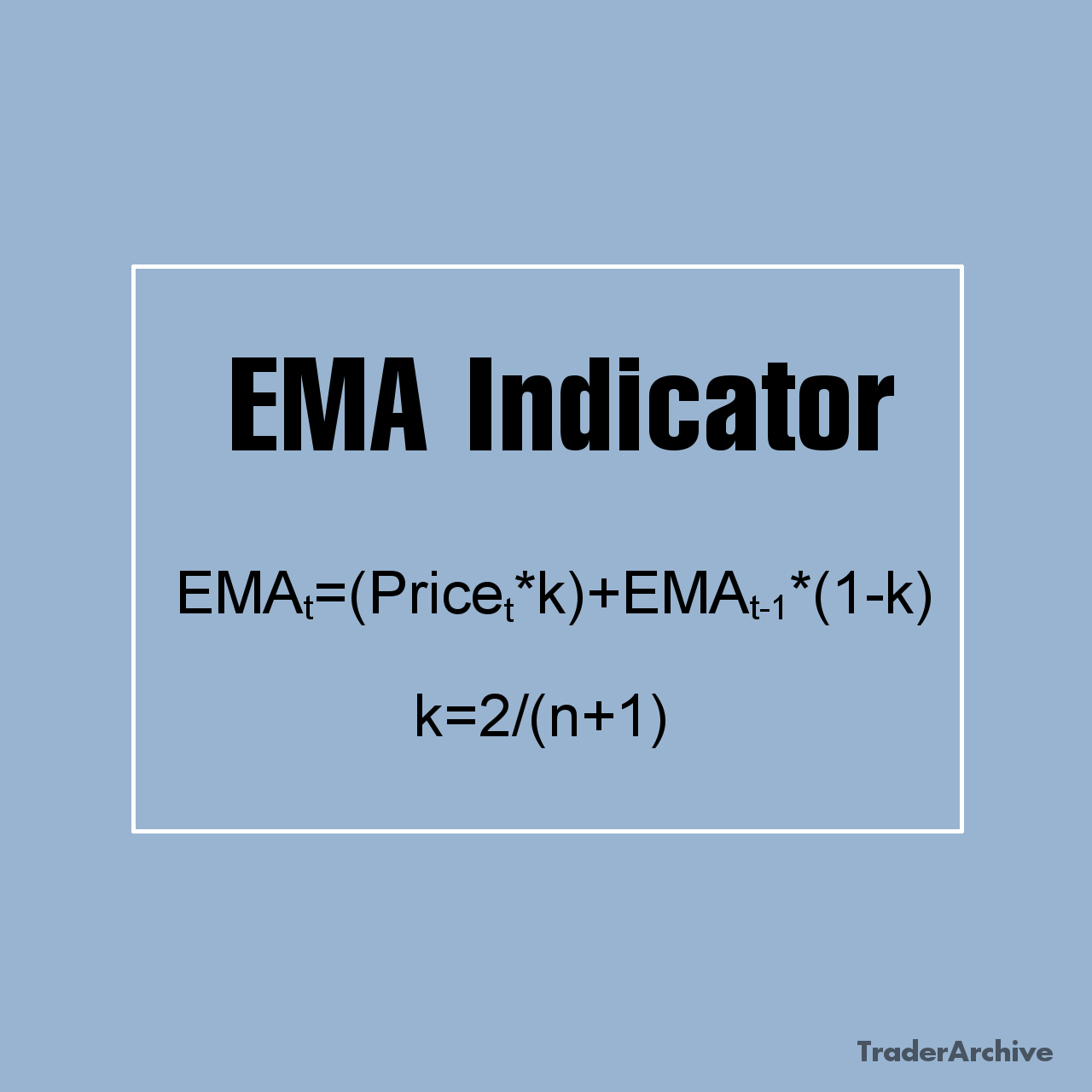
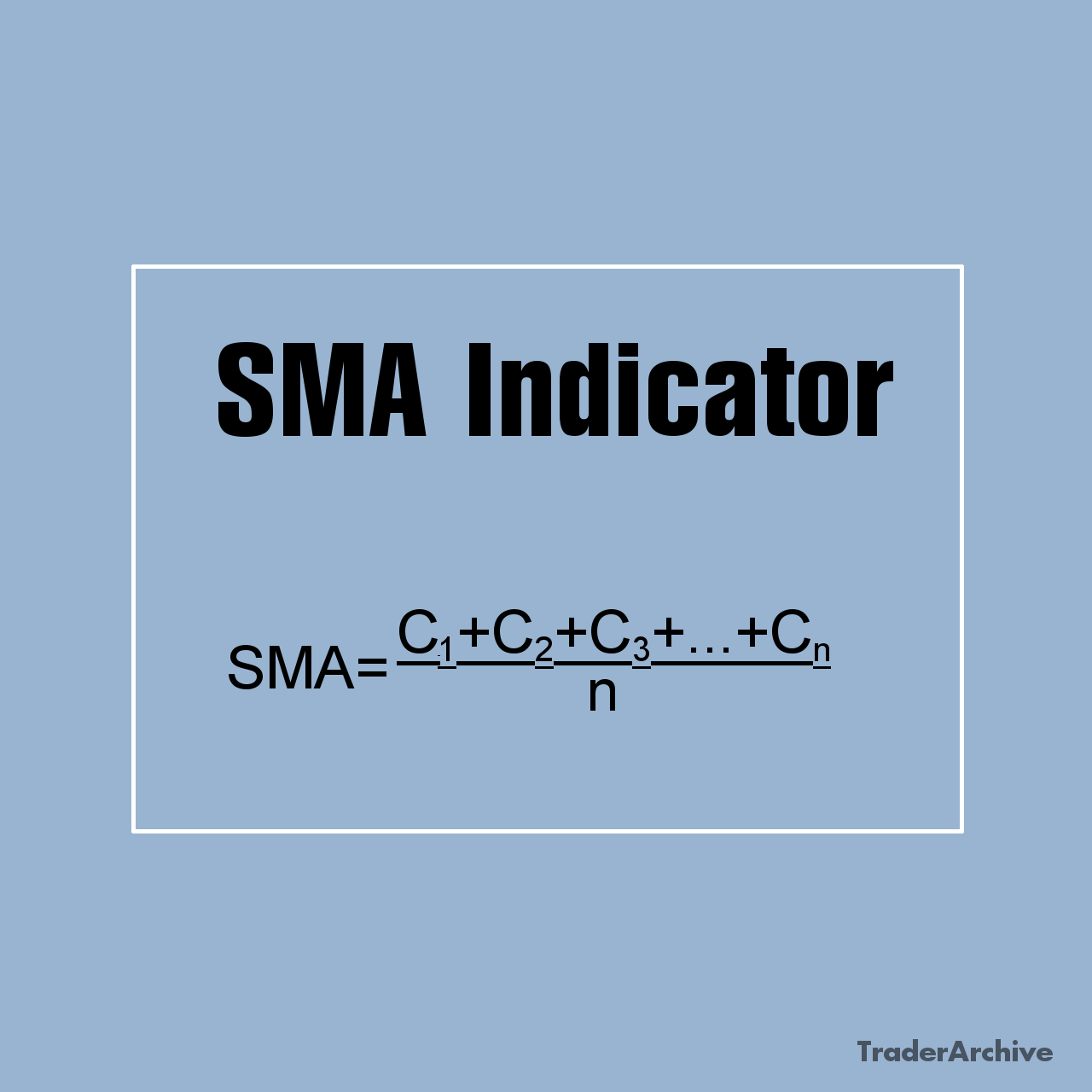
Currency ETFs offer investors an alternative pathway to tap into foreign exchange markets without directly engaging in currency trading. These financial instruments track the performance of single currencies or baskets of currencies and are traded on stock exchanges, providing accessibility to retail investors. Unlike traditional forex trading, where investors speculate on currency pairs, currency ETFs offer a straightforward approach to gaining exposure to individual currencies or currency baskets. In this article, we delve into the mechanics of currency ETFs, explore examples of popular currency ETFs, discuss their associated risks, and provide considerations for investors looking to incorporate them into their portfolios.
Understanding Currency ETF
Currency ETFs are financial instruments that track the performance of a single currency or a basket of currencies. These funds are traded on stock exchanges, making them accessible to retail investors who wish to gain exposure to foreign exchange markets without engaging in direct currency trading.
Unlike traditional forex trading, where investors speculate on currency pairs, currency ETFs offer a simplified approach by providing exposure to individual currencies or currency baskets. For instance, an ETF might track the value of the Euro against the US Dollar (EUR/USD), the Japanese Yen against the US Dollar (JPY/USD), or a basket of emerging market currencies. If an investor purchases shares of a USD/EUR currency ETF, the fund will hold assets denominated in US dollars and euros to replicate the exchange rate between the two currencies. Changes in the exchange rate will directly impact on the value of the ETF shares.
Free Backtesting Spreadsheet
Mechanics of Currency ETFs
Currency ETFs utilize various mechanisms to replicate the performance of the underlying currencies they track. One common method is using currency forward contracts. These contracts allow the ETF issuer to establish a future exchange rate at which they will buy or sell a specific currency.
Another approach involves holding actual currency reserves. In this case, the ETF issuer maintains a reserve of the foreign currency in question, which is used to back the ETF shares. This method is less common due to the logistical challenges and costs associated with holding physical currencies.
Additionally, currency ETFs may employ derivatives such as currency swaps or options to achieve their objectives. These derivatives help manage currency risk and enhance the fund’s performance.
Examples of Currency ETFs
Invesco DB US Dollar Index Bullish Fund
Invesco DB US Dollar Index Bullish Fund (UUP) tracks the performance of the DXY (U.S. Dollar Index), which measures the value of the U.S. dollar relative to a basket of six major foreign currencies. It’s one of the largest and most popular currency ETFs. UUP provides investors with a straightforward and accessible way to gain exposure to the US dollar’s performance relative to a basket of other major currencies. While trading DXY directly may require specialized accounts or access to futures and options markets, UUP can be bought and sold just like any other ETF through a standard brokerage account.
Single Currency ETFs

Comparison of Invesco CurrencyShares Euro Trust (FXE) with EURUSD/TradingView
Invesco CurrencyShares Euro Trust (FXE): This ETF tracks the price of the euro relative to the U.S. dollar. It’s a good option for investors interested in gaining exposure to the eurozone economy.
Invesco CurrencyShares Japanese Yen Trust (FXY): FXY tracks the price of the Japanese Yen relative to the US Dollar. It holds Japanese Yen deposits and seeks to provide exposure to movements in the exchange rate between the Yen and the Dollar.
Invesco CurrencyShares British Pound Sterling Trust (FXB): FXB aims to reflect the performance of the British Pound Sterling relative to the US Dollar. It holds British Pound-denominated deposits to achieve this objective.
Inversed/Leveraged Currency ETF
ProShares UltraShort Yen ETF (YCS): YCS seeks to provide twice the inverse (-2x) of the daily performance of the US Dollar price to the Japanese Yen. Investors bearish on the yen-dollar exchange rate may use YCS to express their views. YCS can be employed for speculative purposes or as a hedging tool against investments with yen exposure.
Cryptocurrency ETFs
ProShares Bitcoin Strategy ETF (BITO). While not a traditional currency ETF, BITO offers indirect exposure to Bitcoin through futures contracts. It’s important to note that Bitcoin is a highly volatile asset class and BITO carries additional risks associated with futures contracts.
iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) is a new type of investment vehicle that began trading in early 2024 and directly invests in Bitcoin, the world’s first and largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization. This ETF offers investors a convenient way to gain exposure to Bitcoin’s price movements without the need to set up a cryptocurrency wallet or exchange account.
This is not an exhaustive list, and there are many other currency ETFs available that track various currencies and baskets of currencies. It’s important to research specific ETFs carefully before investing to understand their investment objectives, fees, and risks.
Risks Associated with Currency ETFs
- Currency Risk: While currency ETFs can be used to hedge against currency risk, they also expose investors to fluctuations in exchange rates. Sudden and unexpected movements in currency markets can result in losses for investors holding currency ETFs.
- Volatility: Currency markets can be highly volatile, driven by factors such as economic data releases, geopolitical events, and central bank policies. As a result, currency ETFs may experience significant price swings, increasing the risk for investors.
- Counterparty Risk: Some currency ETFs use derivatives such as futures contracts to track currency movements. These derivatives expose investors to counterparty risk, the risk that the counterparty to the derivative contract may default on its obligations.
- Leverage Risk: Leveraged currency ETFs amplify the potential returns and risks associated with currency movements. While leverage can magnify profits in favorable market conditions, it can also lead to substantial losses if the market moves against the investor.
- Tracking Error: Currency ETFs aim to track a specific currency or basket of currencies. However, there may be a slight difference between the ETF’s performance and the underlying benchmark it tracks. This difference is known as tracking error.
- Regulatory and Political Risk: Currency markets are influenced by regulatory changes, geopolitical tensions, and political developments. These factors can impact currency ETFs, leading to sudden fluctuations in their value.
Considerations for Investors
- Investment Objectives: Before investing in currency ETFs, investors should define their investment objectives and risk tolerance. Whether seeking diversification, hedging, or speculation, aligning investment decisions with personal financial goals is essential.
- Market Analysis: Conducting thorough market analysis is crucial when investing in currency ETFs. Understanding the factors influencing currency movements, such as economic indicators, geopolitical events, and central bank policies, can help investors make informed decisions.
- Due Diligence: When selecting currency ETFs, investors should perform due diligence on the fund’s holdings, strategy, and performance track record. Assessing factors such as expense ratios, liquidity, and issuer reputation can help identify suitable investment opportunities.
- Portfolio Allocation: Currency ETFs should be integrated into a well-diversified investment portfolio in line with the investor’s overall asset allocation strategy. Balancing exposure to different asset classes, including equities, fixed income, and currencies, can help manage risk and optimize returns.
Final Thoughts
Currency ETFs offer investors an efficient means of gaining exposure to global currency markets, providing access to major currencies like the US dollar and euro, as well as offering inverse or leveraged exposure to suit diverse investment strategies. However, investors should exercise caution and be mindful of the risks associated with currency ETFs, including currency risk, volatility, counterparty risk, leverage risk, tracking error, and regulatory/political risk. By conducting thorough research, aligning investments with personal objectives, and maintaining a diversified portfolio, investors can leverage the benefits of currency ETFs while effectively managing associated risks in their pursuit of investment success.
Share on Social Media: