In recent years, day trading has gained immense popularity. With the advent of online trading platforms and the democratization of financial markets, more and more individuals are venturing into the world of day trading. However, it’s crucial to understand that day trading isn’t a get-rich-quick scheme; it requires discipline, knowledge, and risk management. This comprehensive guide covers the fundamentals of day trading for beginners, equipping you with the necessary tools and insights to enhance your day trading experience.
- Understanding Day Trading
- Getting Started with Day Trading. 8 Initial Steps
- Common Day Trading Strategies
- Technical Analysis for Day Trading
- Challenges and Risks of Day Trading
- Trading Psychology
- Trade Journaling
- Day Trading Options
- Forex Day Trading
- Algorithmic Trading
- Risk Management
- Tax Implications
- Is Day Trading Good for Beginners?
- FAQ
Understanding Day Trading
Day trading involves buying and selling financial instruments such as stocks, currencies, options, or futures within the same trading day, with the goal of profiting from short-term price movements. Unlike traditional investing, which typically involves holding assets for the long term, day traders seek to capitalize on volatility, often making multiple trades in a single day.
One of the key attractions of day trading is the potential for quick profits. By leveraging small price movements, traders aim to generate substantial returns over a short period. However, with this potential reward comes inherent risk. Day trading requires sharp analytical skills, emotional control, and a solid understanding of market dynamics.
As a beginner, it’s advisable to start with a small trading account and gradually scale up as you gain experience and confidence.
Getting Started with Day Trading. 8 Initial Steps
Before diving into day trading, beginners should take the time to educate themselves about the financial markets and trading strategies. Here are some essential steps to get started:
- Learn the Basics: Learn basics of financial markets, trading terminology, and various trading strategies. Familiarize yourself with fundamental concepts such as stocks, options, futures, and forex. Understand how these financial instruments are traded and the factors that influence their prices.
- Choose a Trading Style: Day trading encompasses various styles, including scalping, momentum trading, swing trading, and pattern trading. Explore different approaches to identify the one that aligns with your risk tolerance, personality, and time commitment.
- Choose a Trading Platform: To execute trades, you’ll need to open an account with a reputable brokerage platform that offers robust trading tools, competitive commissions, and reliable customer support. Conduct thorough research to find a platform that suits your needs.
- Practice with a Demo Account: Most brokerage platforms provide simulated trading accounts, allowing beginners to practice trading strategies without risking real capital. Utilize these demo accounts to hone your skills and gain confidence before transitioning to live trading.
- Develop a Trading Plan: A well-defined trading plan serves as your roadmap, outlining your trading objectives, risk management rules, entry and exit criteria, and position sizing strategies. Stick to your plan diligently to minimize impulsive decisions and emotional trading.
- Start Small: As a beginner, it’s advisable to start with a small trading account and gradually scale up as you gain experience and confidence. Avoid risking a significant portion of your capital on single trades, as losses can quickly erode your account balance.
- Manage Risk: Effective risk management is paramount in day trading. Set strict stop-loss orders to limit potential losses on each trade, and adhere to proper position sizing principles to avoid overexposure. Additionally, diversify your trading portfolio to spread risk across multiple assets and strategies.
- Continuous Learning: The financial markets are dynamic and ever-changing, so it’s crucial to stay informed and continuously upgrade your skills. Stay abreast of market developments, economic indicators, and trading strategies through books, online forums, webinars, and financial news outlets.
In addition, successful day traders leverage a suite of tools and resources to analyze markets, including market scanners, news, and research tools. A market scanner helps identify potential trading opportunities by screening stocks based on predefined criteria such as price movements, volume spikes, and technical indicators, enabling traders to filter through thousands of stocks quickly and focus on the most promising ones. Staying informed about market news, earnings reports, economic releases, and corporate developments is crucial. Utilizing news aggregators, financial websites, and research platforms allows traders to access timely information and make informed trading decisions based on current market conditions.
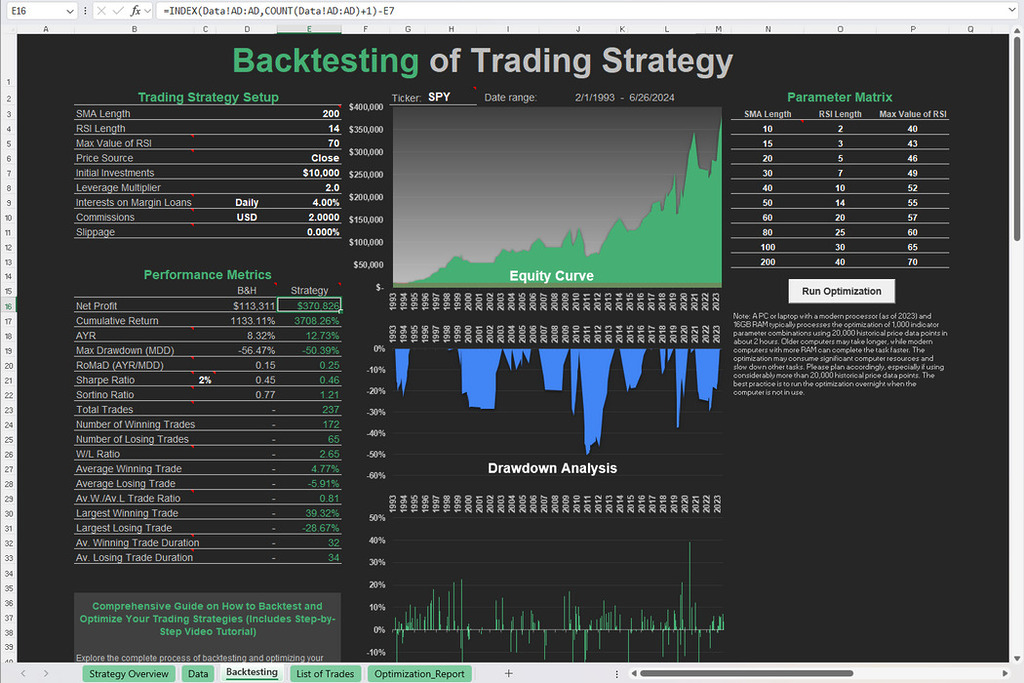
Free Backtesting Spreadsheet
Common Day Trading Strategies
Day traders employ a variety of strategies to capitalize on short-term market movements. While each strategy has its unique characteristics and risk profile, here are some popular day trading strategies for beginners:
- Scalping: Scalping involves executing numerous trades throughout the day to capture small price movements. Traders aim to profit from rapid fluctuations in asset prices, holding positions for only a few seconds to minutes.
- Momentum Trading: This strategy involves identifying and capitalizing on prevailing market trends. Traders look for stocks or other assets that are consistently moving in one direction and aim to ride the trend for as long as possible.
- Breakout Trading: Breakout traders identify key levels of support and resistance and enter positions when the price breaks out of these levels with high volume and momentum. Breakout strategies aim to capture significant price moves following a period of consolidation or range-bound trading.
- Range Trading: Range traders aim to profit from price oscillations within a defined trading range. They buy near the support level and sell near the resistance level, taking advantage of repetitive price patterns and reversals.
- Pullback Trading: Pullback traders look for temporary retracements or pullbacks within the context of an established trend. They enter positions when the price retraces to a key support or resistance level, expecting the trend to resume shortly thereafter.
- Mean Reversion Trading: Mean reversion traders capitalize on temporary deviations from the mean or average price, expecting prices to revert to their historical norms. They identify overbought or oversold conditions using technical indicators and enter contrarian positions accordingly.
- News Trading: News traders capitalize on market-moving events and economic releases by quickly entering and exiting trades based on the news’s impact on asset prices. This strategy requires staying informed about current events and reacting swiftly to market developments.
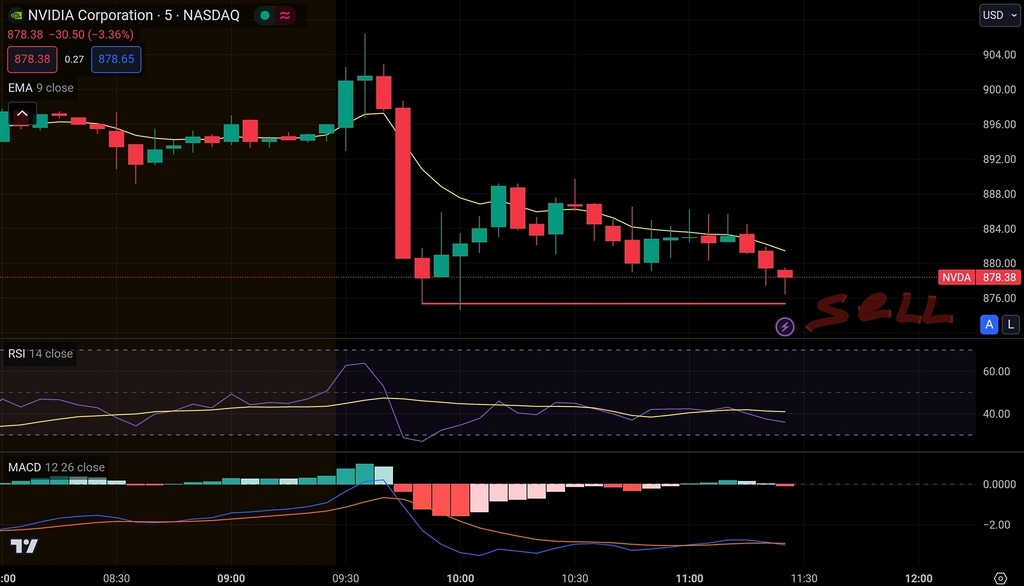
Nvidia intraday price chart with EMA, RSI and MACD indicators in TradingView.
Technical Analysis for Day Trading
Technical analysis is a fundamental aspect of day trading, enabling traders to make informed decisions based on price charts and market data. Unlike fundamental analysis, which focuses on evaluating the intrinsic value of assets, technical analysis examines historical price movements and volume to forecast future price trends. Here’s a breakdown of key components and techniques within technical analysis:
Chart Patterns
Day traders often rely on chart patterns to identify potential trade setups. These patterns, such as triangles, flags, and head and shoulders formations, reflect price movements and market psychology. Recognizing and interpreting these patterns can help traders anticipate price movements and make timely trading decisions.
Indicators for Day Trading
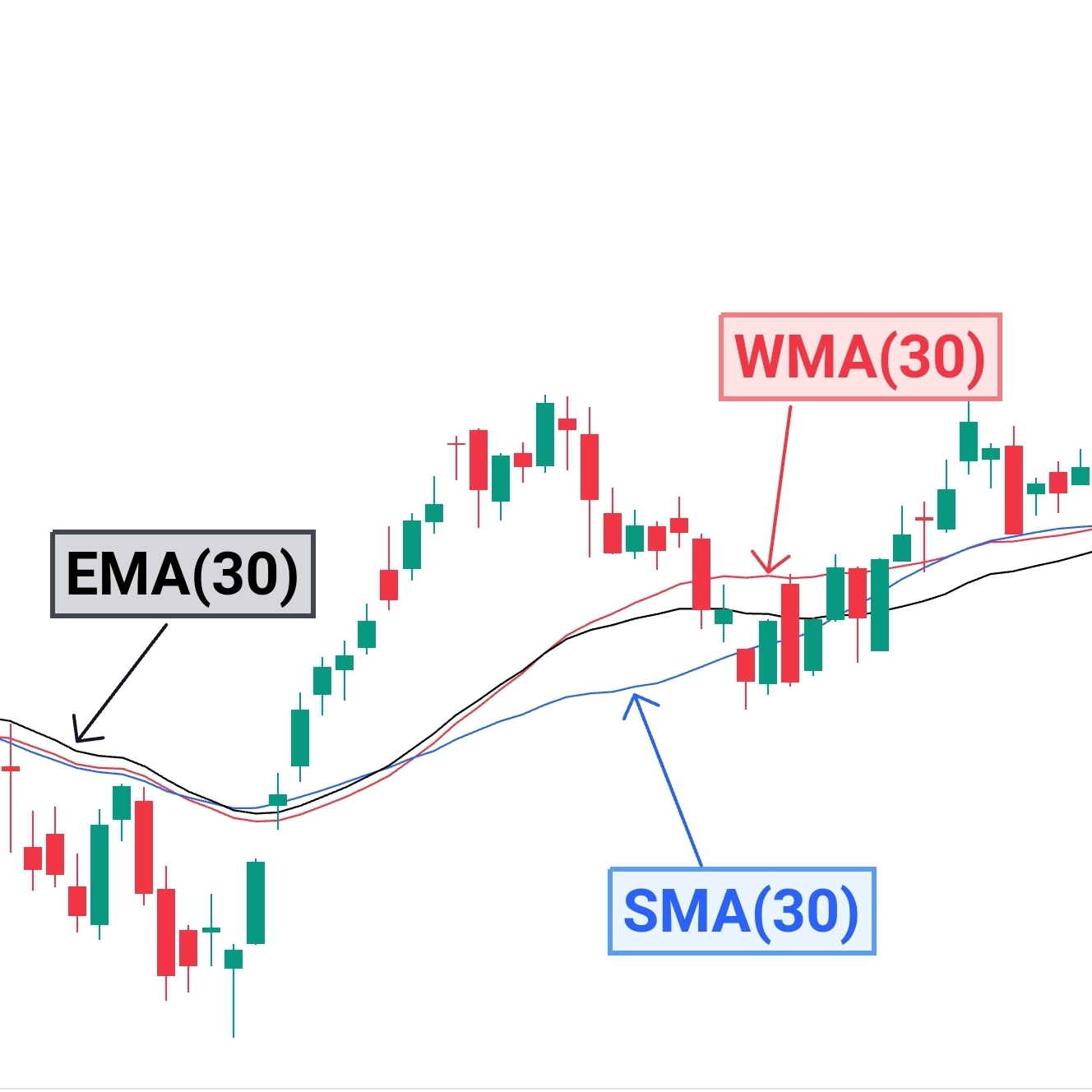
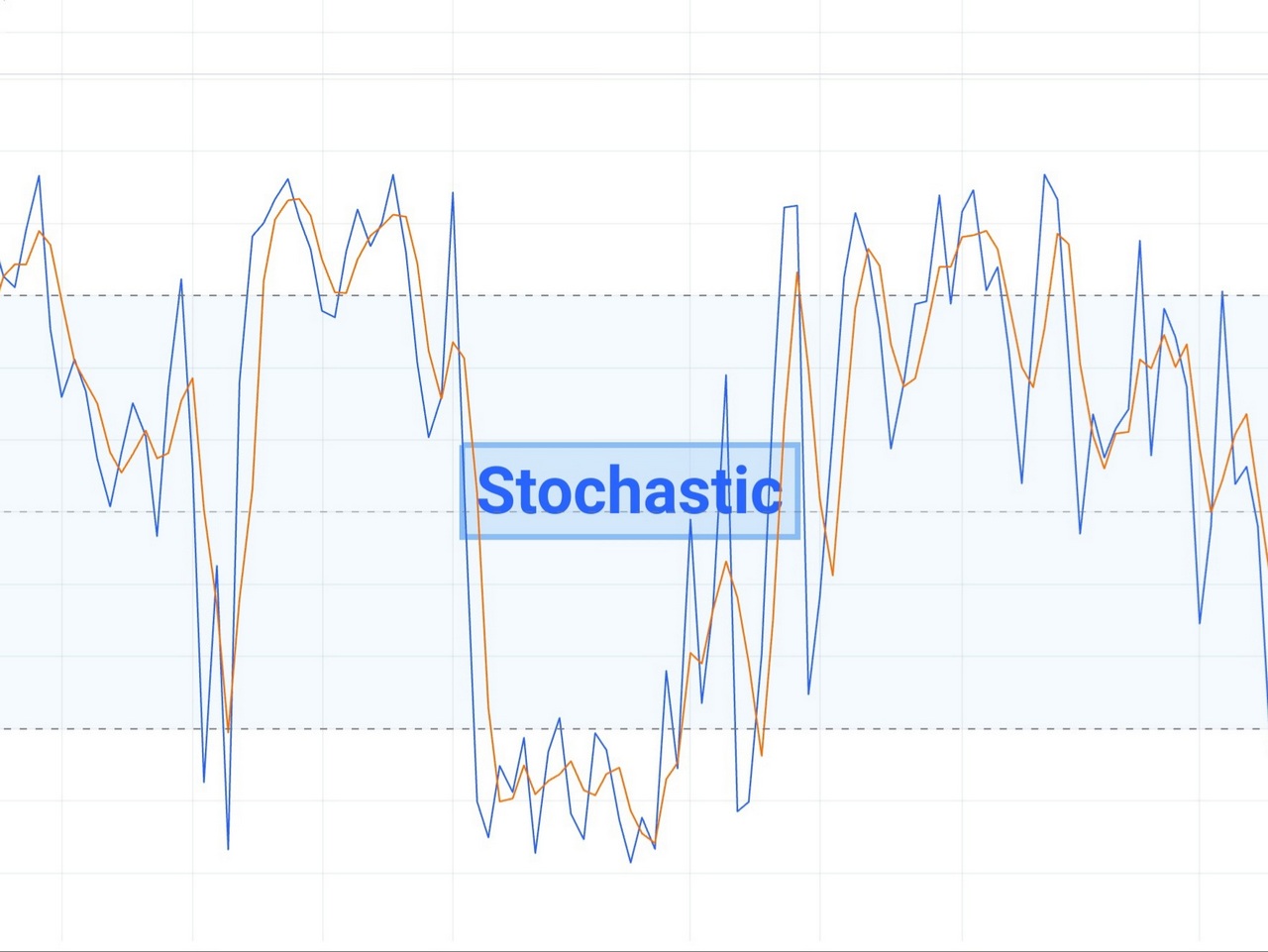
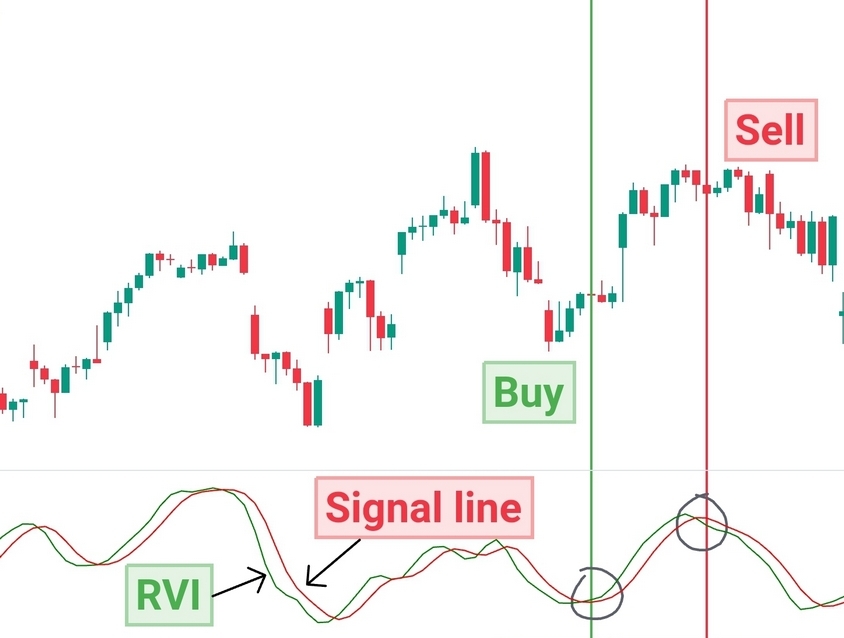
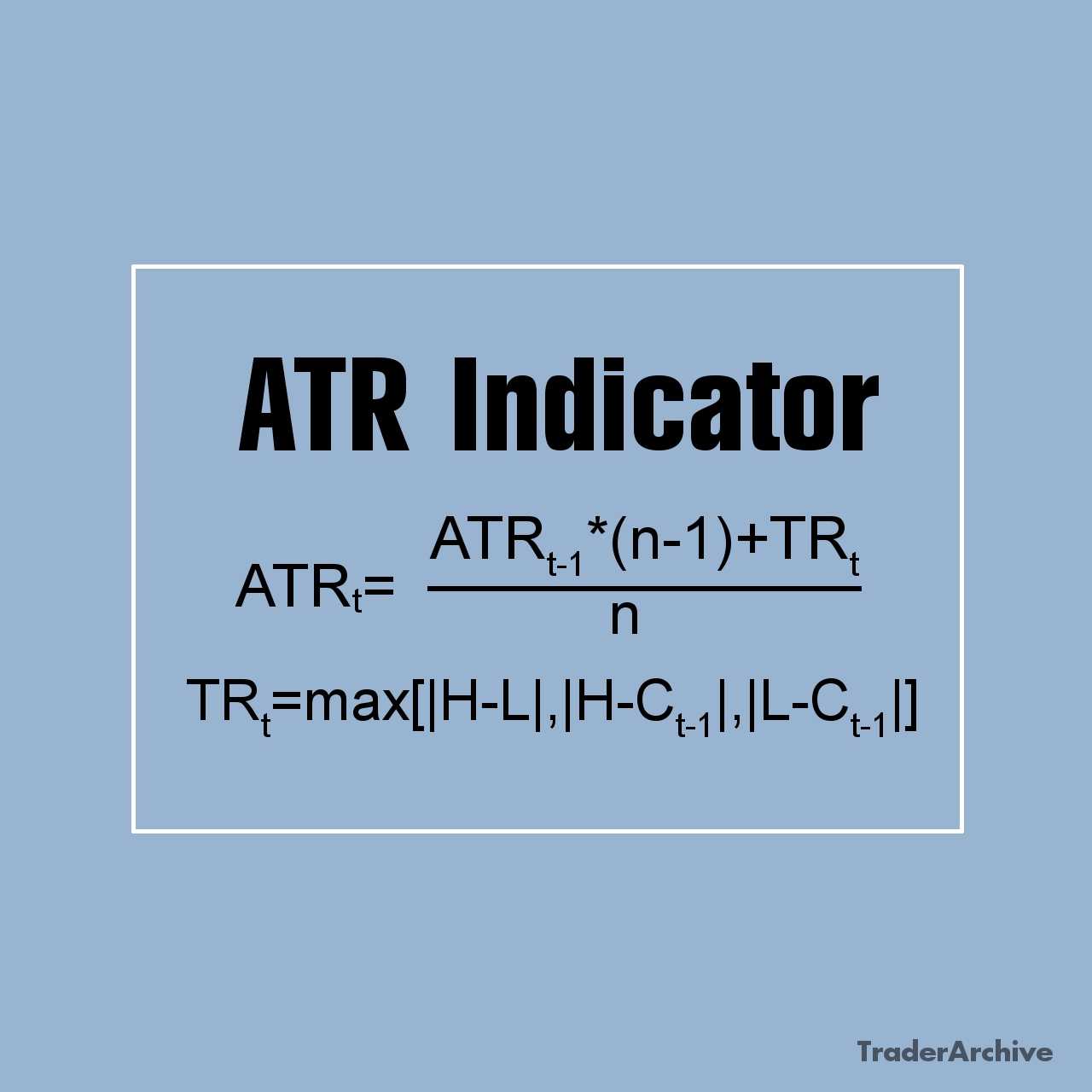
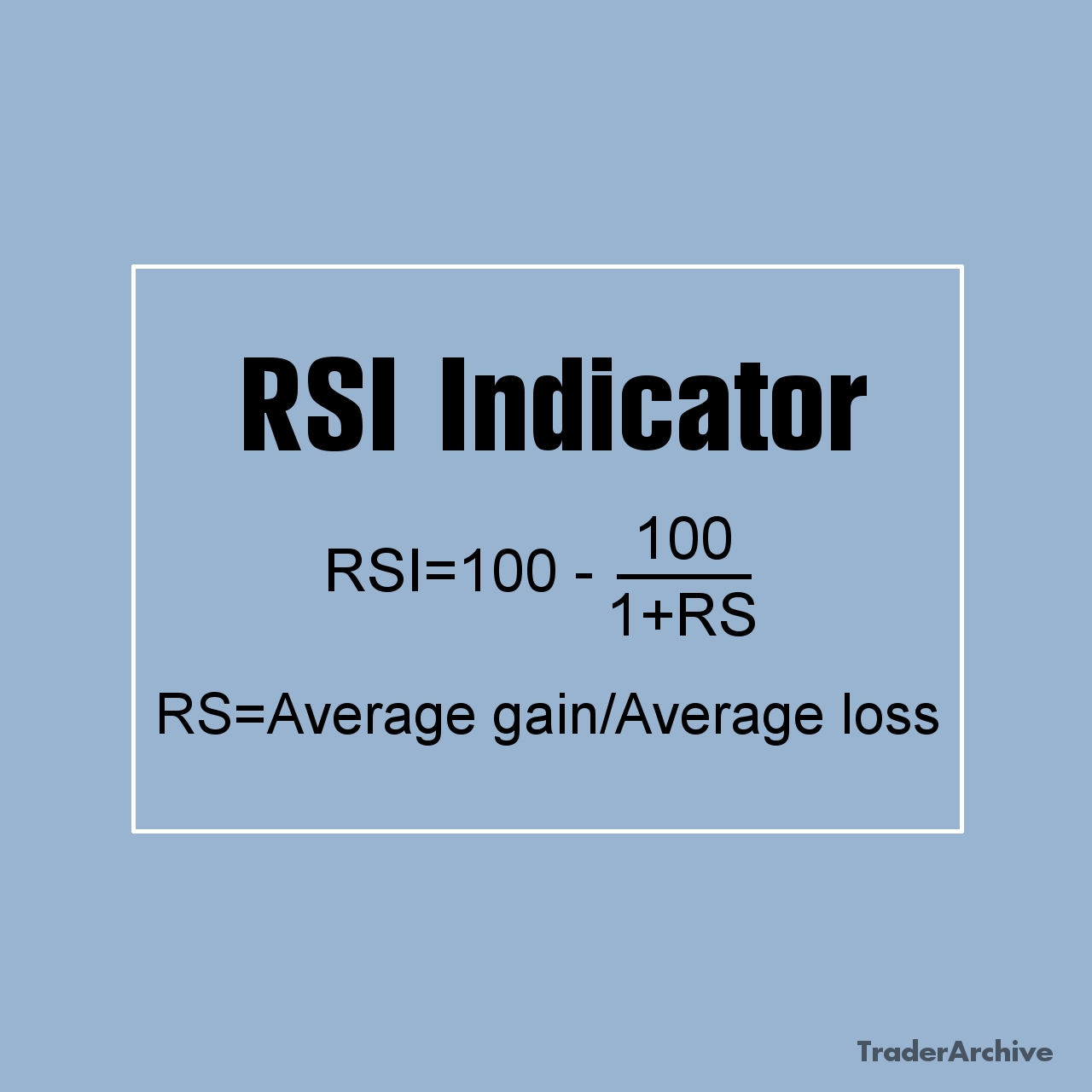
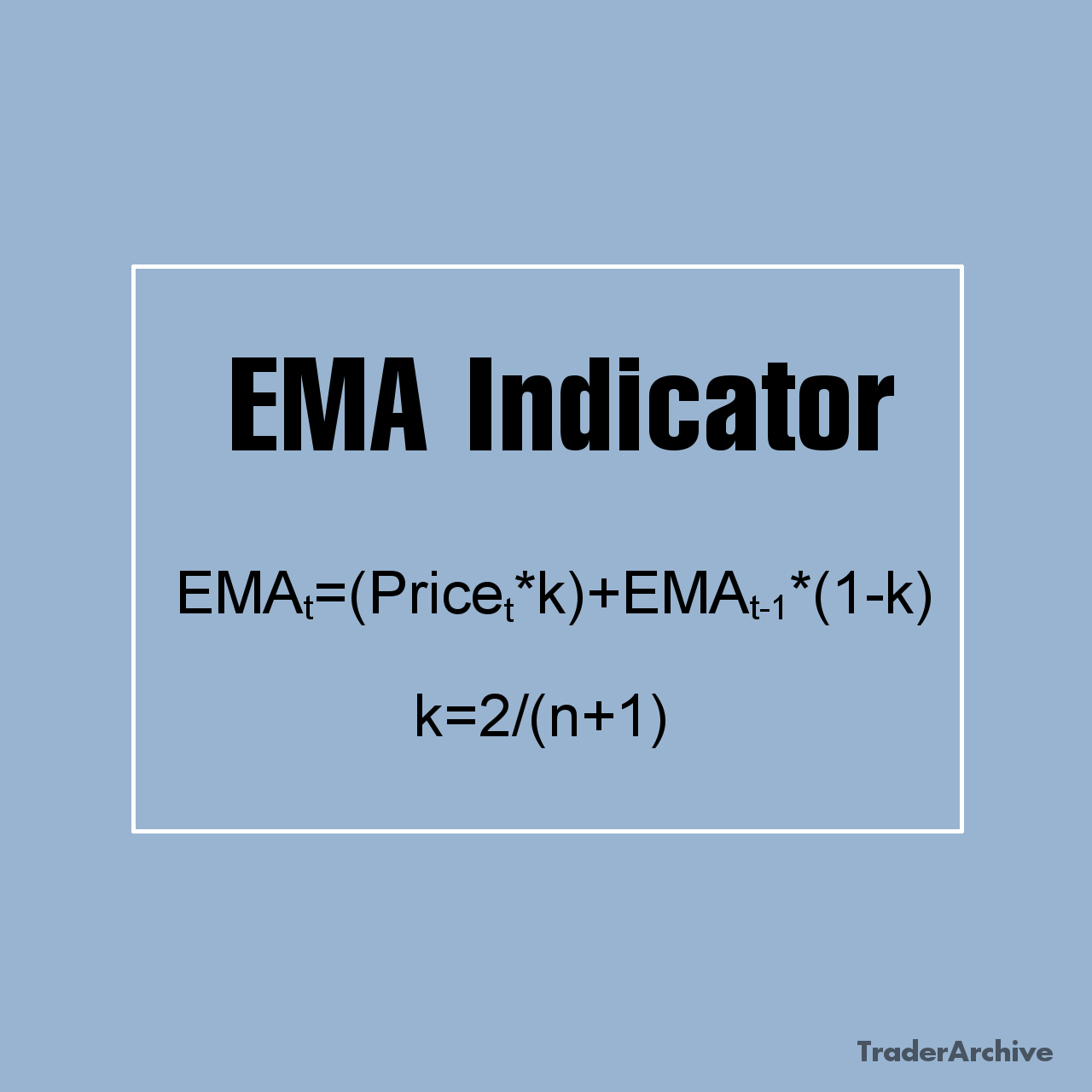
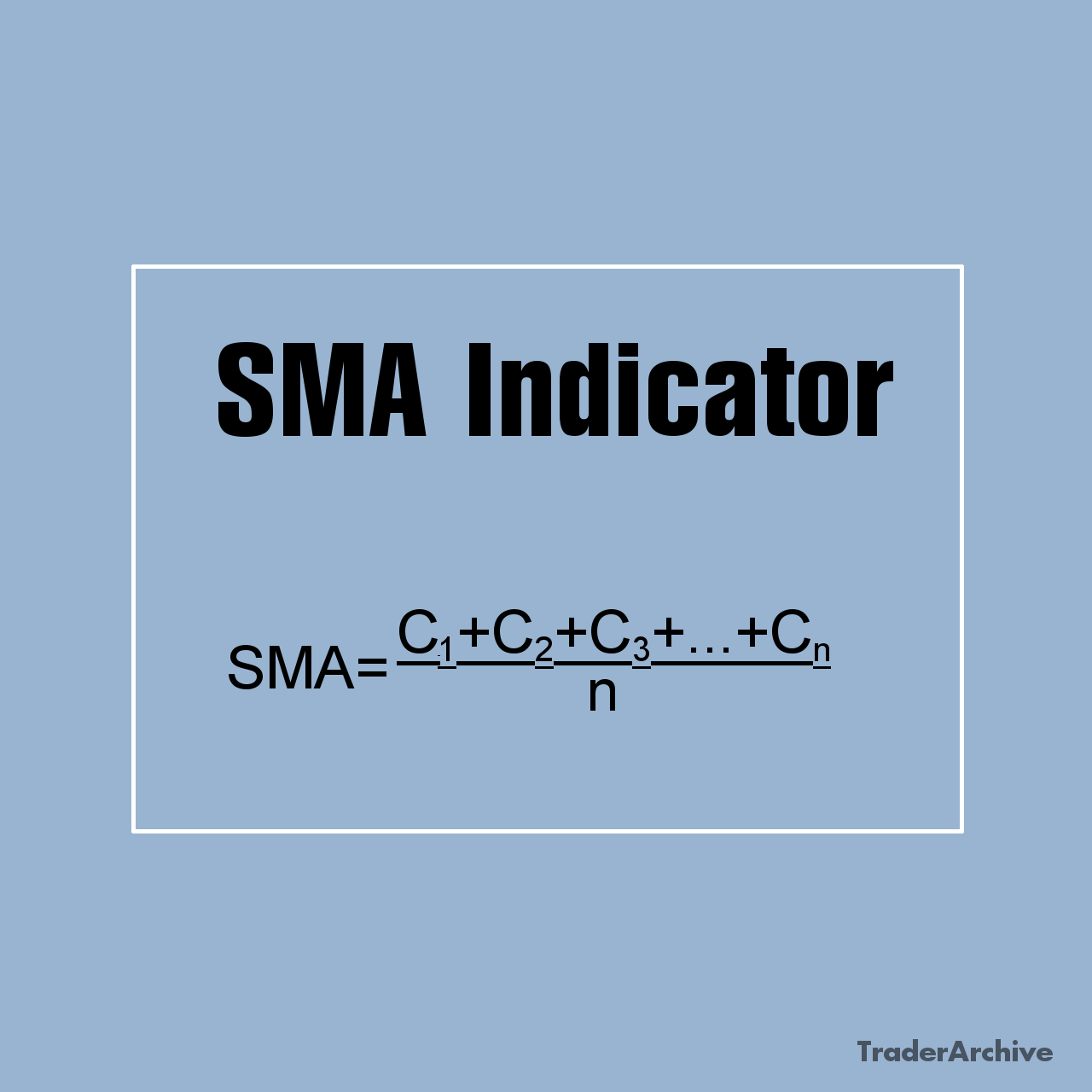
Technical indicators and oscillators are mathematical calculations applied to price charts to provide additional insights into market trends and momentum. Common indicators for day trading include moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), MACD, and stochastic oscillator. Traders use these indicators to confirm trends, detect overbought or oversold conditions, and generate buy or sell signals.
Support and Resistance Levels
Support and resistance levels are key areas on a price chart where buying and selling pressure converge. Support levels represent areas where buying interest outweighs selling pressure, potentially leading to price bounces or reversals. Resistance levels, on the other hand, denote areas where selling pressure exceeds buying interest, often causing price pullbacks or reversals. Identifying and trading off these levels can help traders pinpoint entry and exit points with precision.
Candlestick Patterns
Candlestick patterns provide visual representations of price action within specific timeframes. These patterns, such as doji, hammer, and engulfing patterns, convey market sentiment and potential trend reversals. By analyzing candlestick patterns in conjunction with other technical indicators, traders can gain insights into market dynamics and make more informed trading decisions.
Volume Analysis in Day Trading
Volume analysis involves studying trading volume alongside price movements to gauge the strength and validity of trends. Increasing volume during price advances or declines suggests strong market participation and validates the trend, while decreasing volume may indicate weakening momentum and potential trend reversals. Integrating volume analysis into technical analysis helps traders confirm trade signals and assess market sentiment accurately.
Challenges and Risks of Day Trading
While day trading offers the potential for significant profits, it also comes with inherent risks and challenges that beginners must be aware of:
- Market Volatility: Day trading involves trading in highly volatile markets, where prices can fluctuate rapidly within short timeframes. Volatility can amplify both profits and losses, making risk management crucial for survival.
- Emotional Trading: Emotional decision-making, such as fear, greed, and overconfidence, can cloud judgment and lead to impulsive trades. It’s essential to maintain discipline and stick to your trading plan, regardless of emotional impulses.
- Capital Requirements: Day trading requires sufficient capital to meet margin requirements and withstand potential losses. Beginners with limited capital may face challenges in scaling their trading activities and managing risk effectively.
- Time Commitment: Successful day trading demands a significant time commitment, as traders must monitor markets closely, analyze price movements, and execute trades throughout the trading day. It can be mentally and emotionally taxing, requiring focus and concentration.
- Overtrading: Overtrading, or excessive trading, can deplete trading capital and erode profits due to transaction costs and spread widening. It’s essential to exercise restraint and only trade when high-probability opportunities arise.
- Learning Curve: Day trading has a steep learning curve, and beginners may experience losses as they navigate the complexities of financial markets and develop their trading skills. Patience, perseverance, and continuous learning are essential for long-term success.
One common psychological challenge is the fear of missing out (FOMO), which can tempt traders into chasing trades that do not align with their strategies.
Trading Psychology
Trading psychology plays a crucial role in day trading success. Emotions such as fear, greed, and overconfidence can cloud judgment and lead to impulsive decisions. It’s essential for day traders to develop emotional resilience and maintain discipline in the face of market fluctuations. One common psychological challenge is the fear of missing out (FOMO), which can tempt traders into chasing trades that do not align with their strategies. Conversely, the fear of losing (FOL) can cause traders to exit positions prematurely, missing out on potential profits. To overcome these challenges, traders can implement techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and visualization to stay focused and grounded during trading sessions. Additionally, having a support network of fellow traders or a mentor can provide valuable guidance and accountability.
Trade Journaling
Keeping a trade journal is an invaluable practice for day traders to track their trades, analyze performance, and identify areas for improvement. A trade journal allows traders to document their trading decisions, including entry and exit points, reasons for taking trades, and emotions experienced during each trade. By reviewing past trades, traders can gain insights into their strengths and weaknesses, identify patterns of success or failure, and refine their trading strategies accordingly. Additionally, journaling fosters accountability and discipline by encouraging traders to reflect on their actions and take responsibility for their trading outcomes. Whether using a physical notebook or digital journaling tools, consistent journaling can help traders develop a more disciplined and structured approach to day trading, ultimately leading to greater consistency and profitability.
Day Trading Options
Options are contracts that give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a specific price by a certain expiry date. Day trading options involve opening and closing options positions within the same trading day to capitalize on short-term price movements or market volatility. Day traders can leverage several benefits by incorporating options into their strategies.
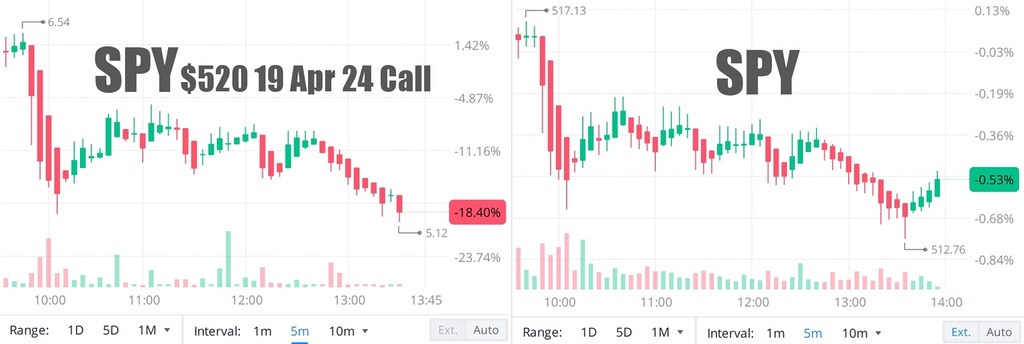
Comparison of SPY ETF and its option contract (1 month before expiry) price changes.
Leverage
Options offer leverage, meaning you can control a larger position in the underlying asset (stock, ETF, etc.) with a smaller upfront investment compared to buying the stock itself. This allows for potentially amplified profits if the market moves in your favor.
Defined Risk
Unlike holding stocks where losses can be significant if the price plummets, options come with a defined maximum loss – the premium you pay for the option. This allows for better risk management and planning for day trading strategies.
Flexibility
Options offer a wider range of strategies compared to simply buying or selling stocks. Day traders can utilize various strategies like calls, puts, spreads (combinations of options), and straddles to profit from different market scenarios – uptrends, downtrends, or even volatile markets.
Speculating on Volatility
Options are well-suited for capitalizing on market volatility, a common occurrence in day trading. By strategically using options, day traders can profit even if the underlying asset’s price movement is relatively small.
Income Generation
Options strategies like selling covered calls allow day traders to generate income by collecting premiums from selling options contracts, even if the price movement doesn’t go exactly as planned.
Interactive Brokers platform for forex day trading
Forex Day Trading
Forex day trading, a subset of day trading, involves speculating on short-term movements in currency exchange rates within a single trading day. Unlike trading stocks or options, forex traders deal directly in currency pairs, such as EUR/USD or GBP/JPY. Here’s a breakdown of forex day trading for beginners:
- Market Access: The forex market is the largest and most liquid financial market globally, operating 24/5, providing ample trading opportunities throughout the day.
- Trading Strategies: Forex day traders employ various strategies similar to day trading other assets, including scalping, trend following, breakout trading, and carry trade.
- Fundamental and Technical Analysis: Both fundamental analysis, considering global economic factors impacting currencies, and technical analysis, using charts and indicators, are crucial for informed forex day trading decisions.
- Volatility: Currency markets can be highly volatile, particularly during news events or economic data releases. Effective risk management is essential to navigate this volatility.
Algorithmic trading eliminates the impact of human emotions from the trading process. By removing emotions such as fear, greed, and other biases, algorithmic trading promotes more disciplined and consistent trading outcomes.
Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading, also known as algo trading or automated trading, utilizes scripts and/or computer programs to analyze market data, identify trading opportunities, and execute trades with minimal human intervention. It offers several benefits to day traders. Algorithmic trading enables traders to automate their strategies to execute trades round the clock. This means traders can take advantage of opportunities in global markets even when they’re not actively monitoring the markets. This technique enables traders to execute orders at lightning-fast speeds, taking advantage of market opportunities that may arise within milliseconds. This rapid execution can be crucial in highly volatile markets where prices can change rapidly. Moreover, algorithmic trading eliminates the impact of human emotions from the trading process. By removing emotions such as fear, greed, and other biases, algorithmic trading promotes more disciplined and consistent trading outcomes.
Risk Management
Successful day traders need effective risk management to protect capital and preserve profitability. Here are some key risk management principles to follow:
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Set stop-loss orders to automatically exit trades at predetermined price levels to limit potential losses. This helps prevent emotions from influencing trading decisions and ensures disciplined risk management.
- Diversify Your Trades: Avoid putting all your capital into a single trade or asset. Diversification helps spread risk across different positions and reduces the impact of any individual trade on your overall portfolio.
- Manage Position Size: Determine the appropriate position size for each trade based on your risk tolerance and account size. Avoid risking more than a small percentage of your capital on any single trade.
- Control Leverage: While leverage can amplify potential profits, it also increases the risk of significant losses. Use leverage cautiously and avoid overleveraging your positions, especially as a beginner trader.
- Stay Disciplined: Stick to your trading plan and avoid making impulsive decisions based on emotions such as fear or greed. Consistent discipline is essential for long-term success in day trading.
Tax Implications
Day trading can have significant tax implications, and it’s essential for traders to understand their tax obligations. Profits from day trading are typically taxed as short-term capital gains, which are subject to higher tax rates than long-term capital gains. Additionally, day traders may be subject to the wash-sale rule, which prohibits them from claiming a tax deduction for losses on a security if they repurchase the same security within 30 days. To navigate these complexities, traders should keep detailed records of their trades, including dates, prices, and quantities. Working with a tax professional who is familiar with the intricacies of day trading can help ensure compliance with tax laws and optimize tax efficiency.
Despite the steep learning curve and the risks involved, day trading offers a unique advantage for beginners: the accelerated pace of learning.
Is Day Trading Good for Beginners?
While it’s commonly acknowledged in various educational resources and books that day trading presents significant challenges, including the potential for losses, it remains an attractive option for beginners. Despite the steep learning curve and the risks involved, day trading offers a unique advantage: the accelerated pace of learning.
Unlike swing trading or long-term investing, where it may take years to accumulate substantial experience, day trading allows beginners to gain valuable insights and practical knowledge within a relatively short timeframe. The rapid turnover of trades exposes traders to a multitude of market scenarios, patterns, and dynamics, facilitating a faster learning process.
It’s true that many beginners incur losses in their initial forays into day trading. However, viewing these losses as a tuition fee for the invaluable education they receive can shift the perspective. By managing risks effectively and approaching each loss as a learning opportunity, beginners can stay afloat and continue refining their trading skills.
Final Thoughts
Day trading can be a rewarding endeavor for those willing to put in the time, effort, and discipline required to succeed. While it offers the potential for substantial profits, it’s essential for beginners to approach day trading with caution, armed with knowledge, risk management skills, and a well-defined trading plan. By leveraging the right tools, adopting proven strategies, and managing risks effectively, aspiring day traders can navigate the challenges of the financial markets and strive for consistent profitability over time. Remember, success in day trading is not guaranteed, but with dedication and perseverance, it’s attainable for those who are willing to put in the work.
Share on Social Media: